Acupuncture & Traditional Chinese Medicine
Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) are components of an ancient medical system that originated in China thousands of years ago. Here’s a summary of each:
Acupuncture:
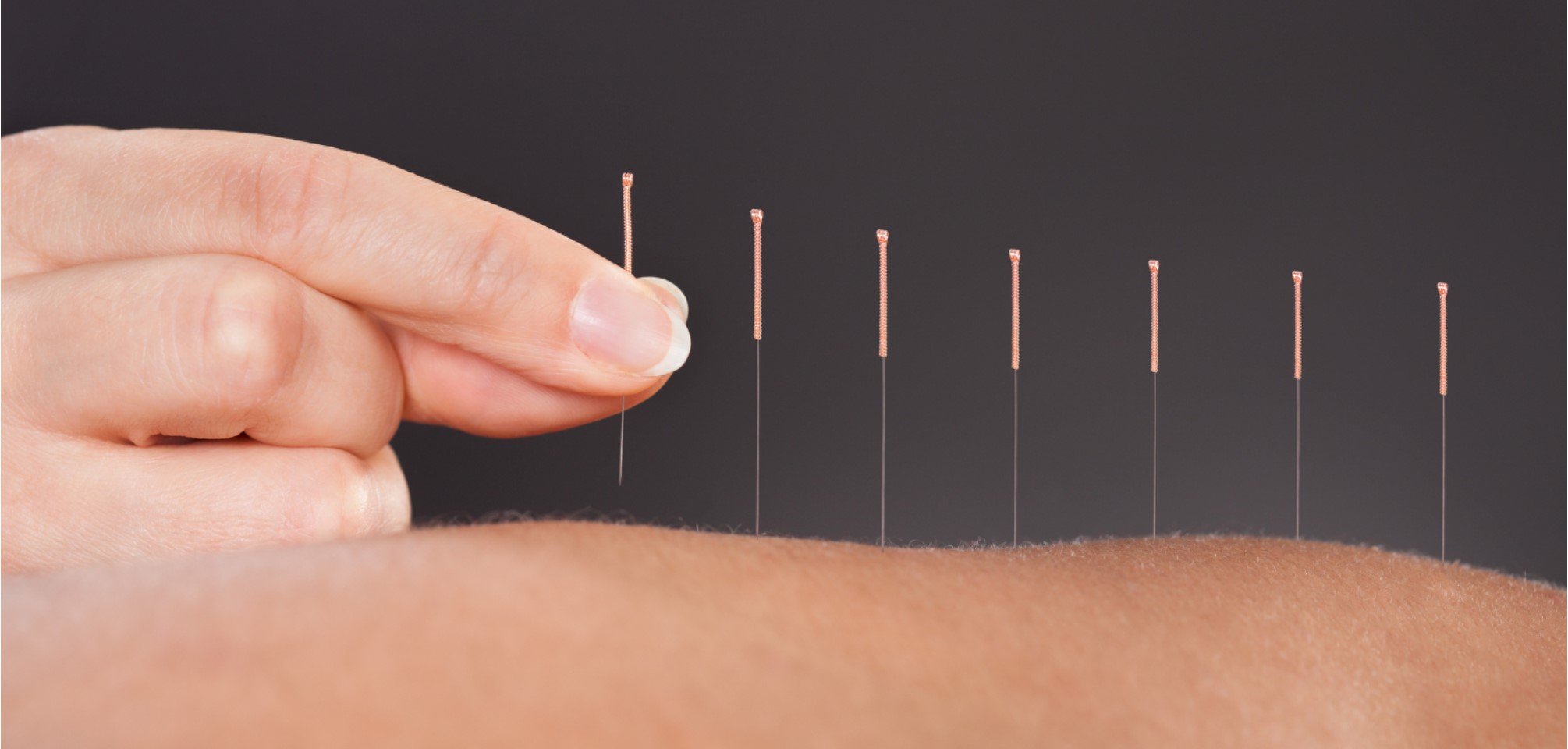
Concept: Involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body, known as acupuncture points, to balance the flow of "qi" (pronounced "chee"), which is believed to be a vital energy or life force.
Purpose: Aims to stimulate the body's natural healing processes, relieve pain, and treat various conditions by correcting imbalances in the flow of qi.
Method: Needles are inserted into points on the body and may be manipulated to achieve the desired effect. The approach is often used for pain management, stress relief, and various other health issues.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM):
Concept: A holistic system that views health as a balance between the body’s essential forces—qi, blood, and bodily fluids—and the environment. It incorporates theories of yin and yang, as well as the five elements (wood, fire, earth, metal, water) to understand and treat health conditions.
Components: Includes acupuncture, guasha, cupping, herbal medicine, dietary therapy, tai chi, and qigong. TCM emphasizes the interconnection of body, mind, and spirit, and the importance of lifestyle and environmental factors in maintaining health.
Diagnosis: Based on observing symptoms, asking detailed questions, and sometimes using methods like pulse diagnosis and tongue examination to assess the balance and flow of qi.
Overall, both acupuncture and TCM focus on promoting balance and harmony within the body to support overall health and well-being.
If you’re curious about Acupuncture and what it can help with, click here.
Guasha
The term "gua sha" translates to "scraping sand," which refers to the technique of scraping or rubbing the skin to stimulate circulation and promote healing. In Western Medicine, it is commonly referred to as “Instrument-Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization” or “muscle scraping”
Method: In TCM, a smooth-edged tool, typically made from materials like jade, quartz, or ceramic, is used to apply pressure and scrape the skin in specific patterns. This is usually done on areas of the body where muscle tension or pain is present.
Purpose: Gua Sha aims to improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and release stagnant qi (energy) and blood. It's thought to help alleviate pain, enhance immune function, and promote overall wellness.
Appearance: The scraping action can sometimes leave red or purple marks on the skin, known as "sha," which are often temporary and fade over a few days. These marks are a sign that the treatment is working to release toxins and stimulate blood flow.
Use: It can be used for various purposes, including relieving muscle pain, reducing inflammation, and improving the function of internal organs. It is also sometimes employed as part of a broader treatment plan for respiratory or digestive issues.
TCM Cupping
You may already be familiar with cupping, but in TCM, cupping is believed to help improve the flow of qi (vital energy), blood, and lymphatic fluids, and to release muscle tension and stagnation.
Method: Glass, bamboo, or silicone cups are typically used. There are two main techniques:
Dry Cupping: Involves creating a vacuum inside the cups by heating them with fire (traditional method) or using a pump (modern method), and then placing them on the skin. The suction draws the skin and underlying tissues into the cup. This technique of cupping can be stationary or moving. In the office, glass cups are used for fire cupping.
Wet Cupping: Involves a similar process, but with small punctures made in the skin before applying the cups. The suction then draws out a small amount of blood, which is believed to help expel toxins.
Purpose: Cupping is used to:
Improve Circulation: The suction helps increase blood flow to the area where the cups are applied, which can aid in healing and reduce muscle soreness.
Relieve Pain: It is often used for musculoskeletal pain, such as back pain or stiffness.
Reduce Inflammation: By improving blood flow and reducing stagnation, cupping may help decrease inflammation.
Promote Relaxation: The process can help relieve stress and promote a sense of relaxation.
Support Detoxification: Some believe that the removal of toxins and improved circulation aid in detoxifying the body.
Appearance: Cupping can leave red or purple marks on the skin where the cups were placed. These marks are often called “cupping marks” or “sha,” and they generally fade within a few days to a week.